Acromegaly Cats And Dogs
Acromegaly Cats And Dogs - Cat Meme Stock Pictures and Photos
Dunning m d, lowrie c s, bexfield n h et al (2009) exogenous insulin treatment after hypofractionated radiotherapy in cats with.
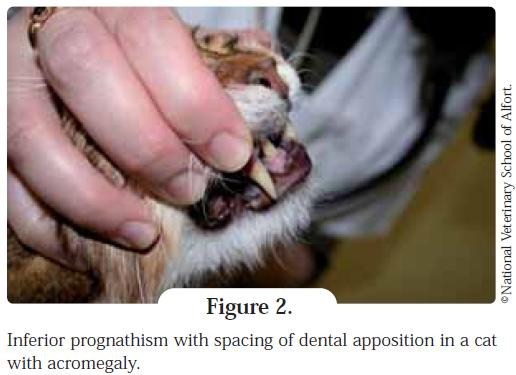
Acromegaly cats and dogs. The diagnosis of acromegaly was confirmed by demonstration of extremely high basal serum growth hormone concentrations (22 to 131 micrograms/l) in all cats. The soft tissues at the back of the cat’s mouth can increase in size, making it hard for them to breath. Further reading publications refereed papers.
And the diabetes that does develop tends to be relatively unresponsive to treatment with normal doses of insulin. Acromegaly is an endocrine disease that leads to elevated production and secretion of growth hormone (gh). In dogs, acromegaly results after administration of progestational compounds for the suppression of oestrus in intact female dogs.
Net weight gain of lean body mass in cats with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus is a key sign of. Cats and people usually have a pituitary tumor which is the cause of acromegaly. Therefore, polydipsia, polyuria, and polyphagia are the most common presenting signs.
The definitive diagnosis is confirmed by imaging and checking the blood level of certain hormones. Find details on acromegaly in dogs including diagnosis and symptoms, pathogenesis, prevention, treatment, prognosis and more. Request pdf | acromegaly in dogs and cats | acromegaly is an endocrine disease that leads to elevated production and secretion of growth hormone (gh).
Acromegaly, or hypersomatotropism, results from chronic, excessive secretion of growth hormone in the adult animal. The disorder triggers the pituitary gland to overproduce somatotropin, a growth hormone (gh). Excessive production of a hormone.
The tumour is usually benign and very slow growing. 2022 aaha pain management guidelines for dogs and cats. The pituitary gland secretes the growth hormone thanks to the stimulation of another.