Neoplasia In Cats Bladder
Neoplasia In Cats Bladder - Cat Meme Stock Pictures and Photos
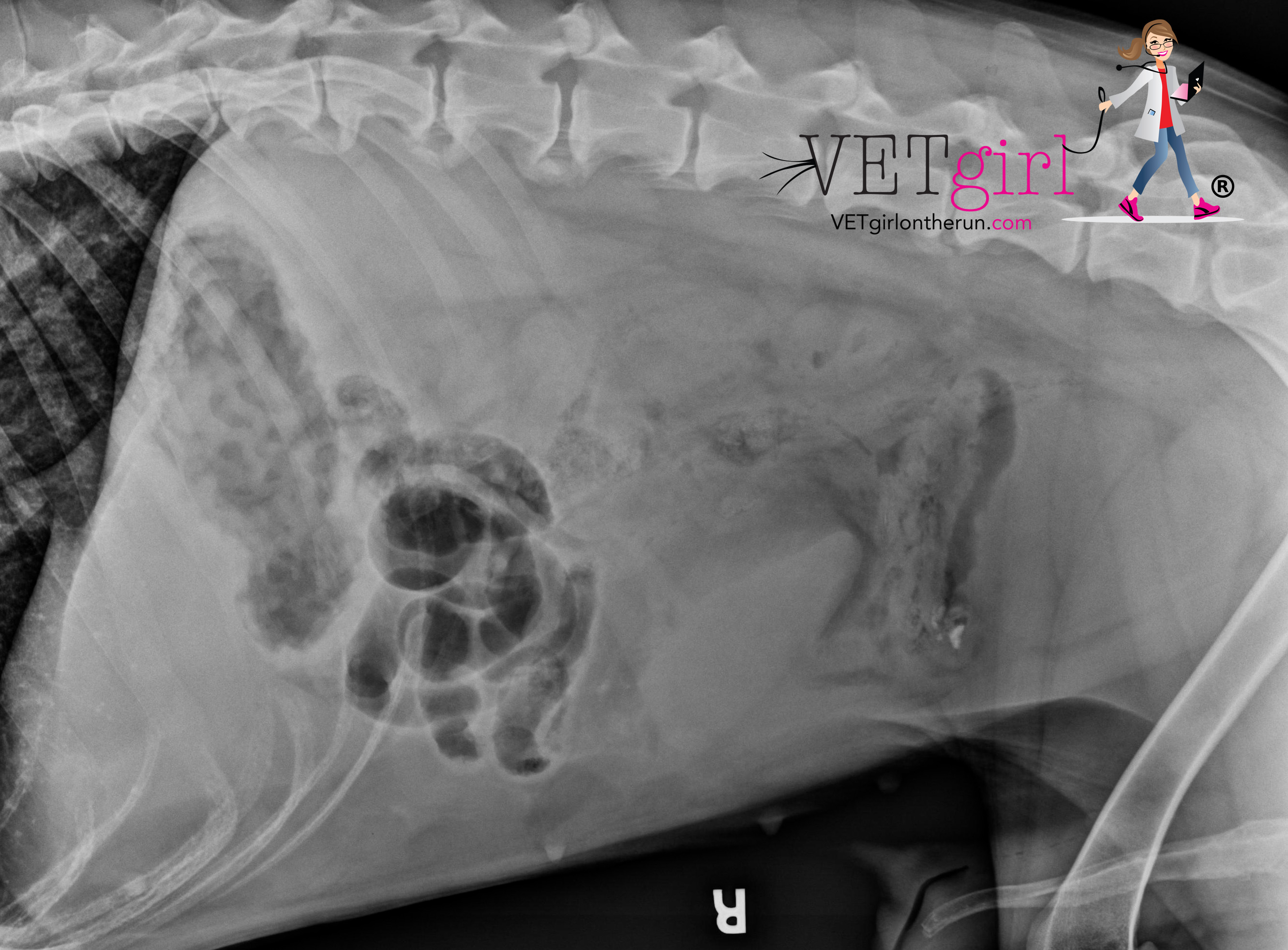
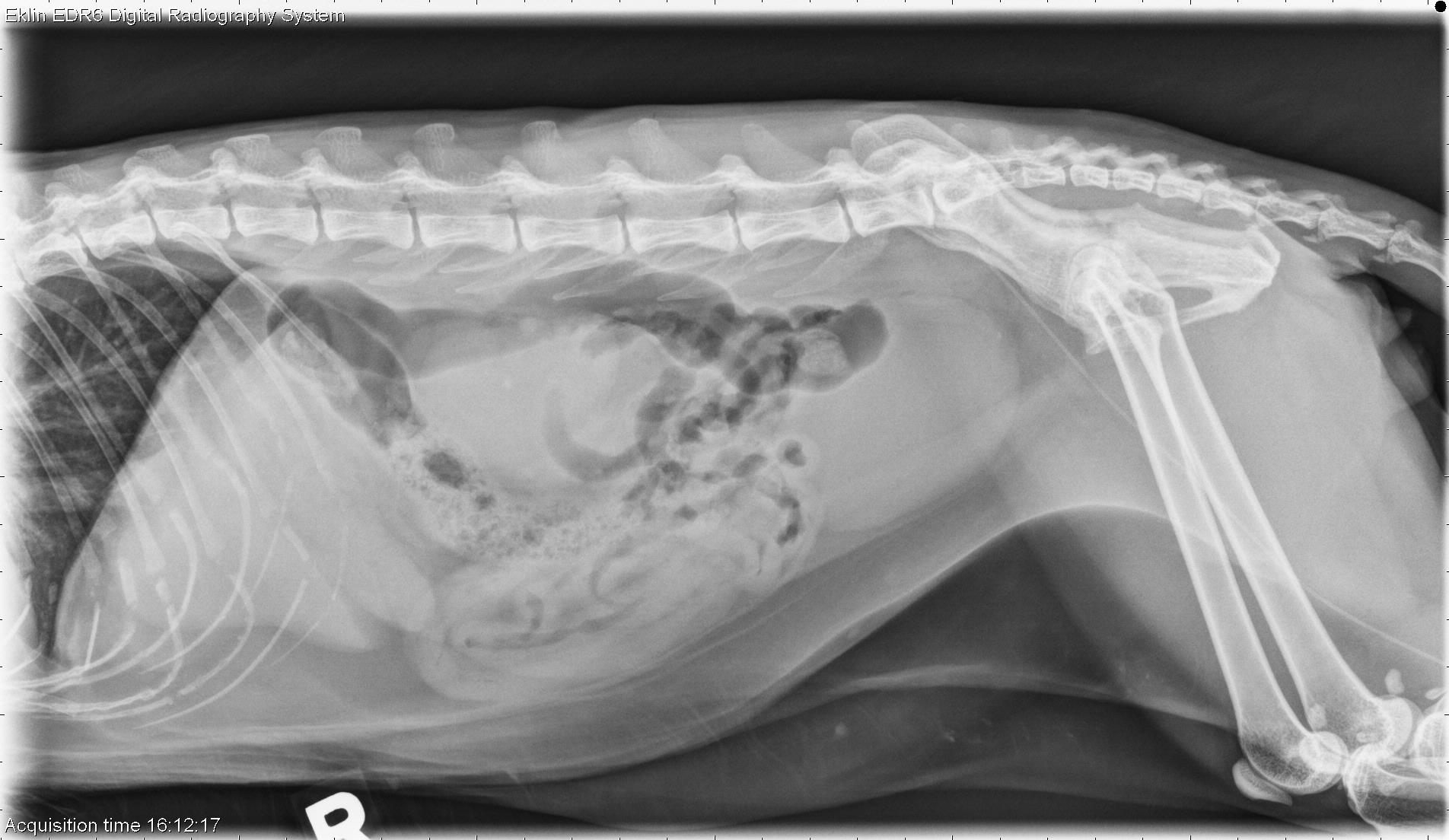
Transitional cell carcinoma of the lower urinary tract in dogs.
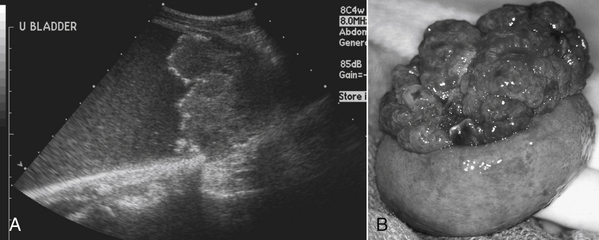
Neoplasia in cats bladder. They are more likely to be malignant than benign. The diagnosis of a urinary bladder neoplasm is generally delayed because of a lack of. A bladder tumour is a benign or cancerous tumour of the bladder or urethra of cats.
The low incidence in cats may be due to a difference in tryptophan metabolism that results in low urinary concentrations of carcinogenic tryptophan metabolites. Neoplasms of the canine and feline urinary bladder are diagnostic and therapeutic challenges to the veterinary clinician. 3 certain breeds may have an increased risk of specific etiologies of flutd;
Colorado state university, veterinary teaching hospital, fort collins 80523. In dogs, the most common type of urinary tract tumors are bladder tumors, and of these, the most common is transitional cell carcinoma (tcc). The mean age of affected dogs and cats is 9 yr.
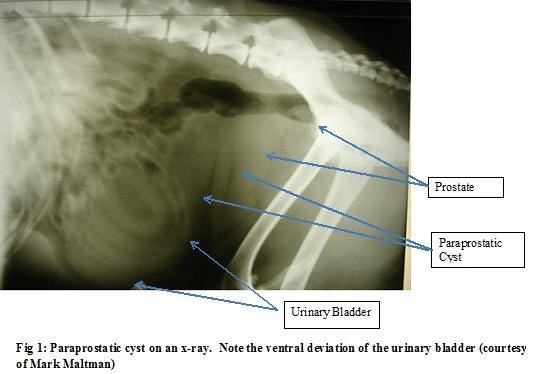
Swalec k m, smeak d d, baker a l (1989) urethral leiomyoma in a cat. Barrand k r (1999) rectal prolapse associated with urinary bladder neoplasia in a cat. The following list includes possible options that your vet will discuss with you depending on the type of cancer, location, whether it is benign or malignant, what to expect long term, quality of life, ongoing costs, and.
For example, in some studies, russian blue, himalayan, and persian breeds have had an increased risk of. Patnaik a k, schwarz p d & greene r w (1986) a histopathological study of 20 urinary bladder neoplasms in the cat. A case of feline rectal prolapse which appeared to be secondary to transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder is described.
Urinary bladder neoplasia in the dog and cat. In general, tcc is an aggressive, highly invasive. If there is a lesion in the bladder wall, the bacteria can penetrate it and grow into a bacterial colony, therefore causing an infection.